

Heavy alcohol use can damage all organ systems, but it particularly affects the brain, heart, liver, pancreas and immune system. Predominant diagnostic classifications are alcohol use disorder ( DSM-5) or alcohol dependence ( ICD-11) these are defined in their respective sources. Because there is disagreement on the definition of the word alcoholism, it is not a recognized diagnostic entity, and the use of alcoholism terminology is discouraged due to its heavily stigmatized connotations. Mental illness, delirium, Wernicke–Korsakoff syndrome, irregular heartbeat, cirrhosis of the liver, cancer, fetal alcohol spectrum disorder, suicide Īlcohol cessation typically with benzodiazepines, counselling, acamprosate, disulfiram, naltrexone Alcoholics Anonymous (AA) and other Twelve Step Programs, AA/Twelve Step Facilitation (AA/TSF) ģ80 million / 5.1% adults (2016) Īlcoholism is, broadly, any drinking of alcohol that results in significant mental or physical health problems. Psychiatry, clinical psychology, toxicology, addiction medicineĭrinking large amounts of alcohol over a long period, difficulty cutting down, acquiring and drinking alcohol taking up a lot of time, usage resulting in problems, withdrawal occurring when stopping 1915: "Ah! When will we be rid of alcohol?" (f) certain symptoms, for which supplementary information is provided, that represent important problems in medical care in their own right.Alcohol addiction, alcohol dependence syndrome, alcohol use disorder (AUD) Ī French temperance organisation poster depicting the effects of alcoholism in a family, c.(e) cases in which a more precise diagnosis was not available for any other reason.(d) cases referred elsewhere for investigation or treatment before the diagnosis was made.
(c) provisional diagnosis in a patient who failed to return for further investigation or care.
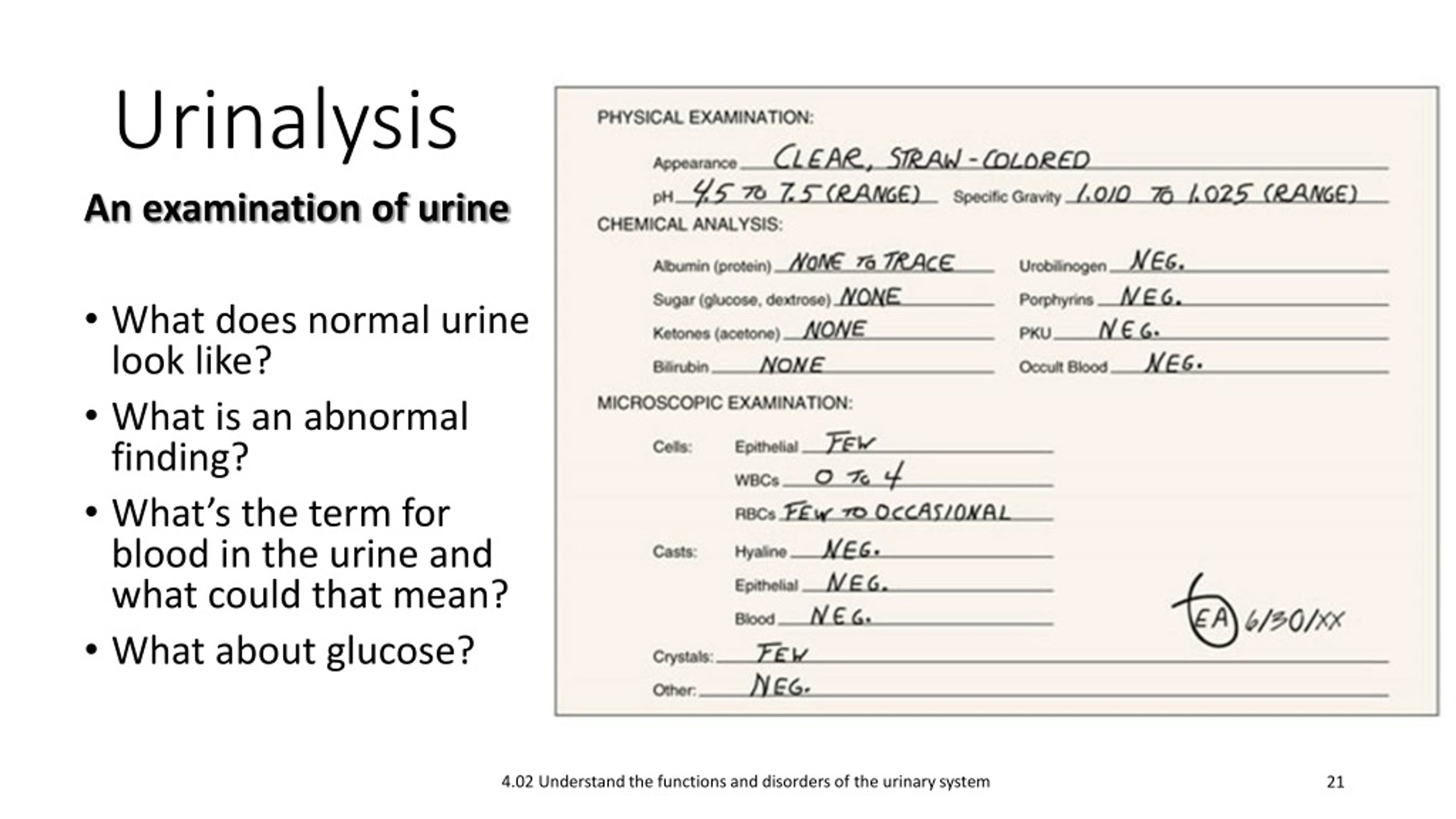


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
